
Abstract:
The emergence of large-scale freeform shapes in architecture poses big challenges to the fabrication of such structures. A key problem is the approximation of the design surface by a union of patches, socalled panels, that can be manufactured with a selected technology at reasonable cost, while meeting the design intent and achieving the desired aesthetic quality of panel layout and surface smoothness. The production of curved panels is mostly based on molds. Since the cost of mold fabrication often dominates the panel cost, there is strong incentive to use the same mold for multiple panels. We cast the major practical requirements for architectural surface paneling, including mold reuse, into a global optimization framework that interleaves discrete and continuous optimization steps to minimize production cost while meeting user-specified quality constraints. The search space for optimization is mainly generated through controlled deviation from the design surface and tolerances on positional and normal continuity between neighboring panels. A novel 6-dimensional metric space allows us to quickly compute approximate inter-panel distances, which drastically improves the performance of the optimization and enables the handling of complex arrangements with thousands of panels. The practical relevance of our system is demonstrated by paneling solutions for real, cuttingedge architectural freeform design projects.
Results:
 |
|||
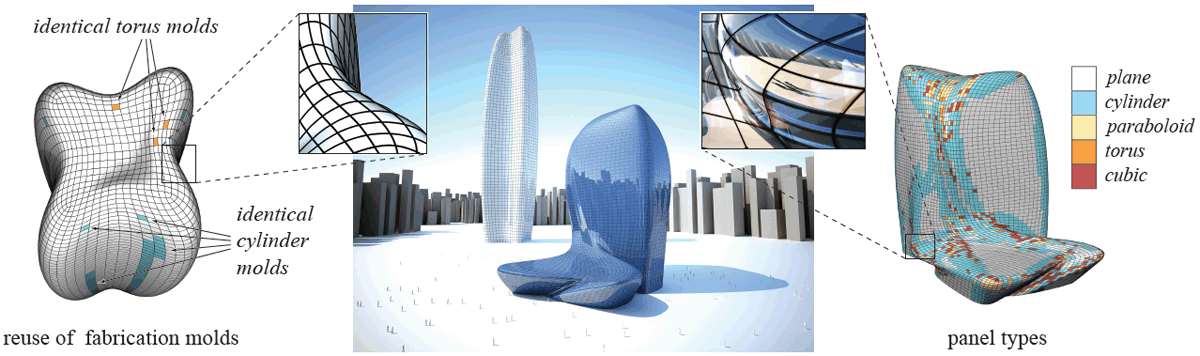
| (Figure above) Rationalization of large-scale architectural freeform surfaces with planar, single-, or double-curved panels. Our algorithm computes a paneling solution that meets prescribed thresholds on positional and normal continuity, while minimizing total production cost. Reuse of molds (left) and predominant use of simple panels (right) are important drivers of the optimization. (Left: Zaha Hadid Architects, Lilium Tower, Warsaw. Right: Zaha Hadid Architects, National Holding Headquarters, Abu Dhabi.) | |||
 |
|||
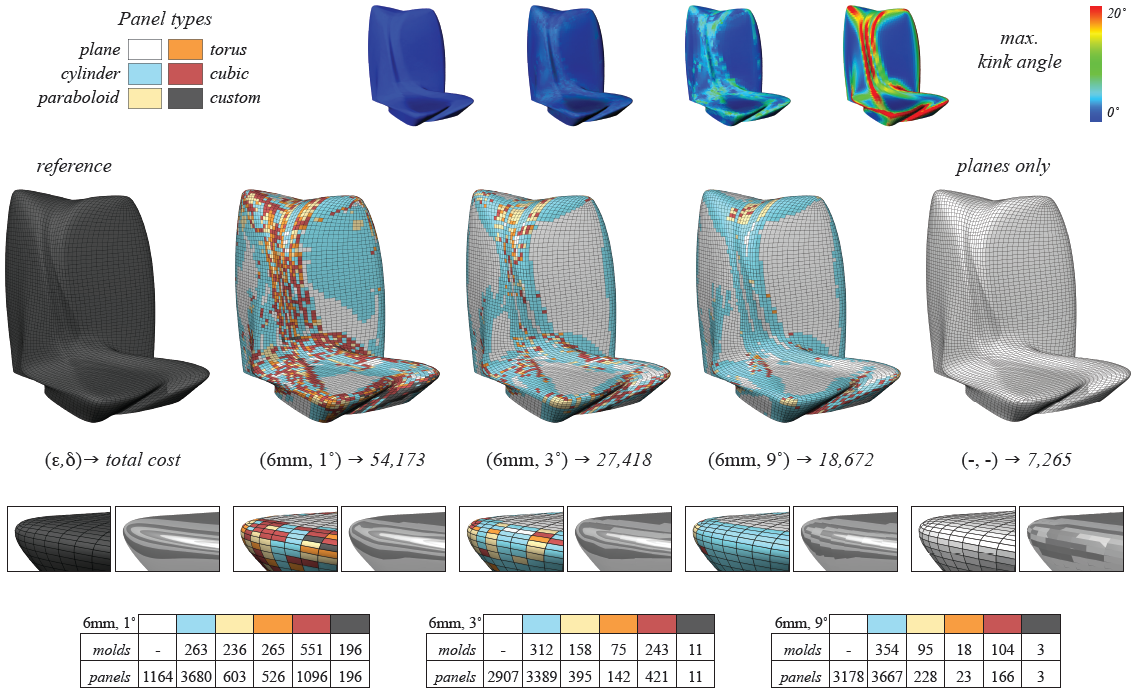
| (Figure above) Paneling results with varying kink angle thresholds \delta and fixed divergence thresholds \epsilon = 6mm for the design of the National Holding Headquarters. The images on the right show a solution using only planar panels of which 3,796 do not meet the prescribed divergence threshold. The zooms show reflection lines to illustrate inter-panel continuity which successively improves with lower kink angle thresholds. | |||
 |
|||
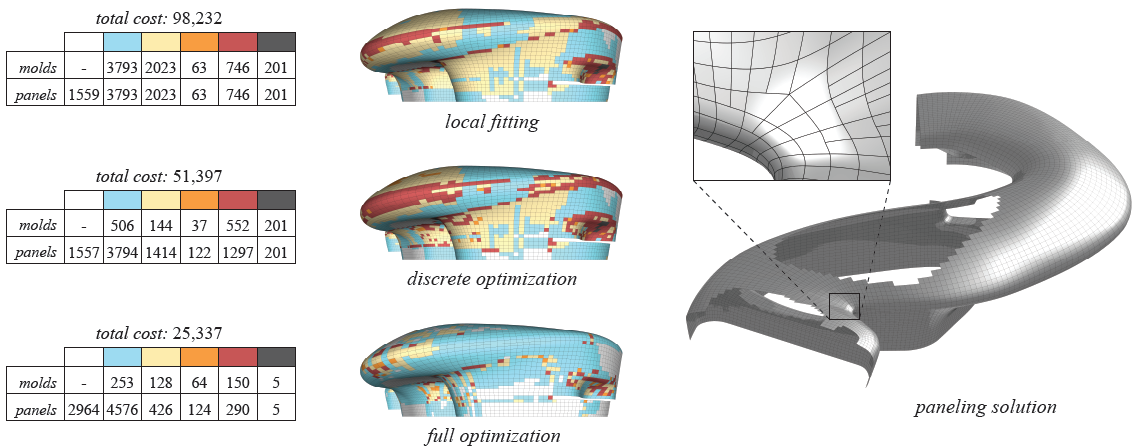
| (Figure above) Comparison of different methods for the same quality thresholds. State-of-the-art commercial tools only support a greedy panel assignment based on local fitting (top). Just one single application of our discrete optimization greatly reduces cost without loss in surface quality (middle). The full paneling algorithm interleaving discrete optimization with global continuous registration produces a high quality paneling (bottom). This solution contains 90% single curved panels and a very small number of custom molds, leading to a significantly reduced cost compared to greedy and local methods. The zoom on the right shows that our algorithm supports arbitrary curve network topology, including t-junctions. (Zaha Hadid Architects, Dongdaemun Design Plaza and Park, Seoul.) | |||
| |||
| |||
Bibtex:
@article{eksmpm_paneling_sig_10,
AUTHOR = "Michael Eigensatz and Martin Kilian and Alexander Schiftner and Niloy J. Mitra and Helmut Pottmann and Mark Pauly",
TITLE = "Paneling Architectural Freeform Surfaces",
JOURNAL = "ACM Transactions on Graphics",
VOLUME = "29",
NUMBER = "4",
pages = {45:1--45:10},
articleno = {45},
numpages = {10},
YEAR = "2010",
}
|
|