Non-local Scan Consolidation for 3D Urban Scenes
Qian Zheng, Andrei Sharf, Guowei Wan, Yangyan Li, Niloy J. Mitra, Daniel Cohen-Or, Baoquan Chen
ACM SIGGRAPH 2010
Abstract:
Recent advances in scanning technologies, in particular devices
that extract depth through active sensing, allow fast scanning of
urban scenes. Such rapid acquisition incurs imperfections: large
regions remain missing, significant variation in sampling density is
common, and the data is often corrupted with noise and outliers.
However, buildings often exhibit large scale repetitions and selfsimilarities.
Detecting, extracting, and utilizing such large scale
repetitions provide powerful means to consolidate the imperfect
data. Our key observation is that the same geometry, when scanned
multiple times over reoccurrences of instances, allow application of
a simple yet effective non-local filtering. The multiplicity of the geometry
is fused together and projected to a base-geometry defined
by clustering corresponding surfaces. Denoising is applied by separating
the process into off-plane and in-plane phases. We show that
the consolidation of the reoccurrences provides robust denoising
and allow reliable completion of missing parts. We present evaluation
results of the algorithm on several LiDAR scans of buildings
of varying complexity and styles.
Results:
 |
|
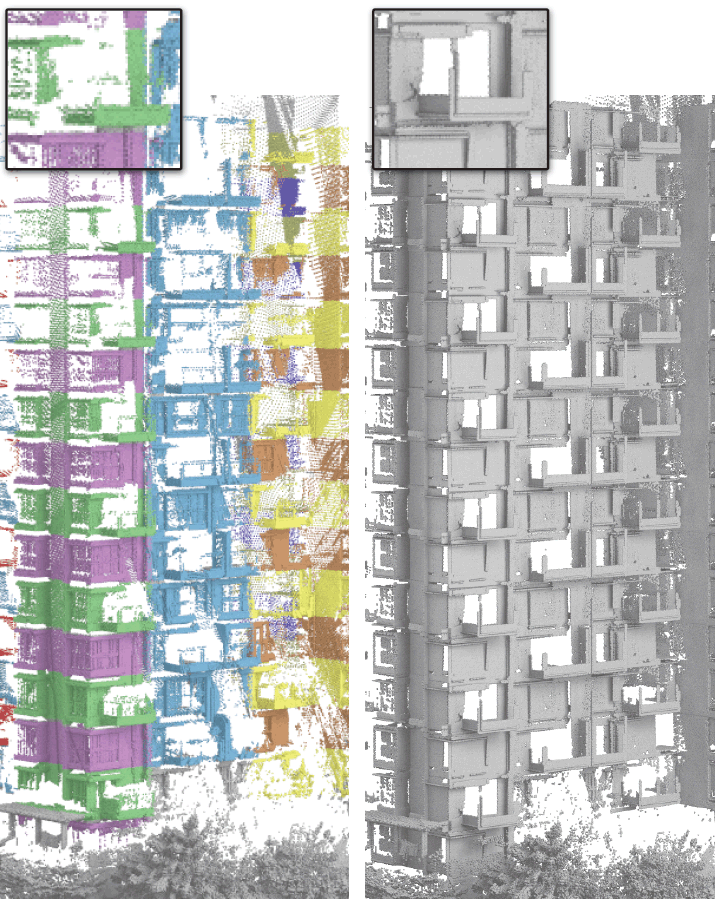
Consolidating a LiDAR scan captured 3D building containing
noise and missing regions. (Left) Repeated parts are detected
and colored. (Right) Result of non-local filtering and consolidation
of the repeated parts. |
|
| |
|
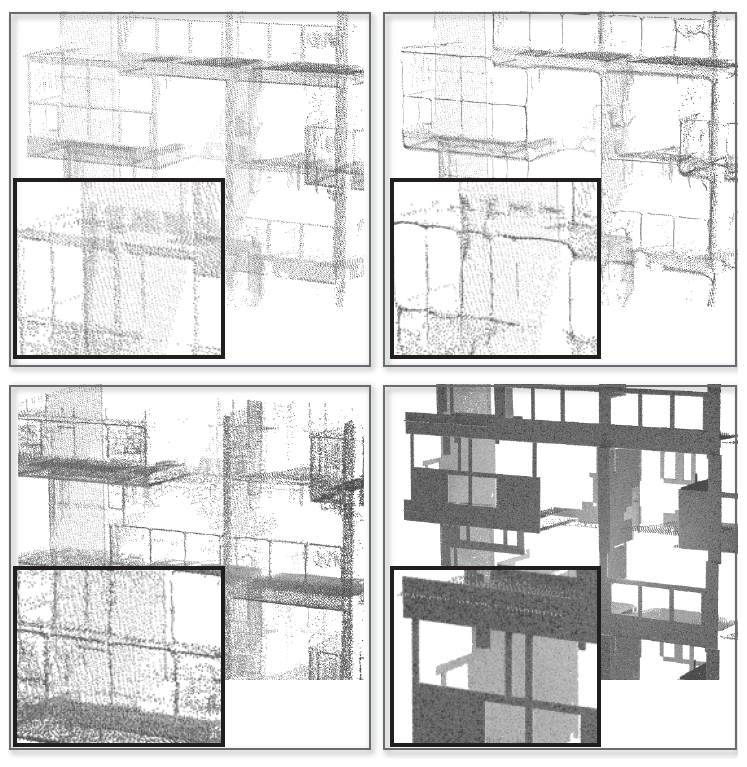
Comparison with state-of-the-art point consolidation
method. The input (top-left), result using WLOP [Huang et al.
2009] (top-right), result using WLOP on the union of detected repetitions
aligned to one instance (bottom-left), and result using our
consolidation method (bottom-right). Respective zooms for one
balcony are shown.
| |
 |
|
| |
 |
|
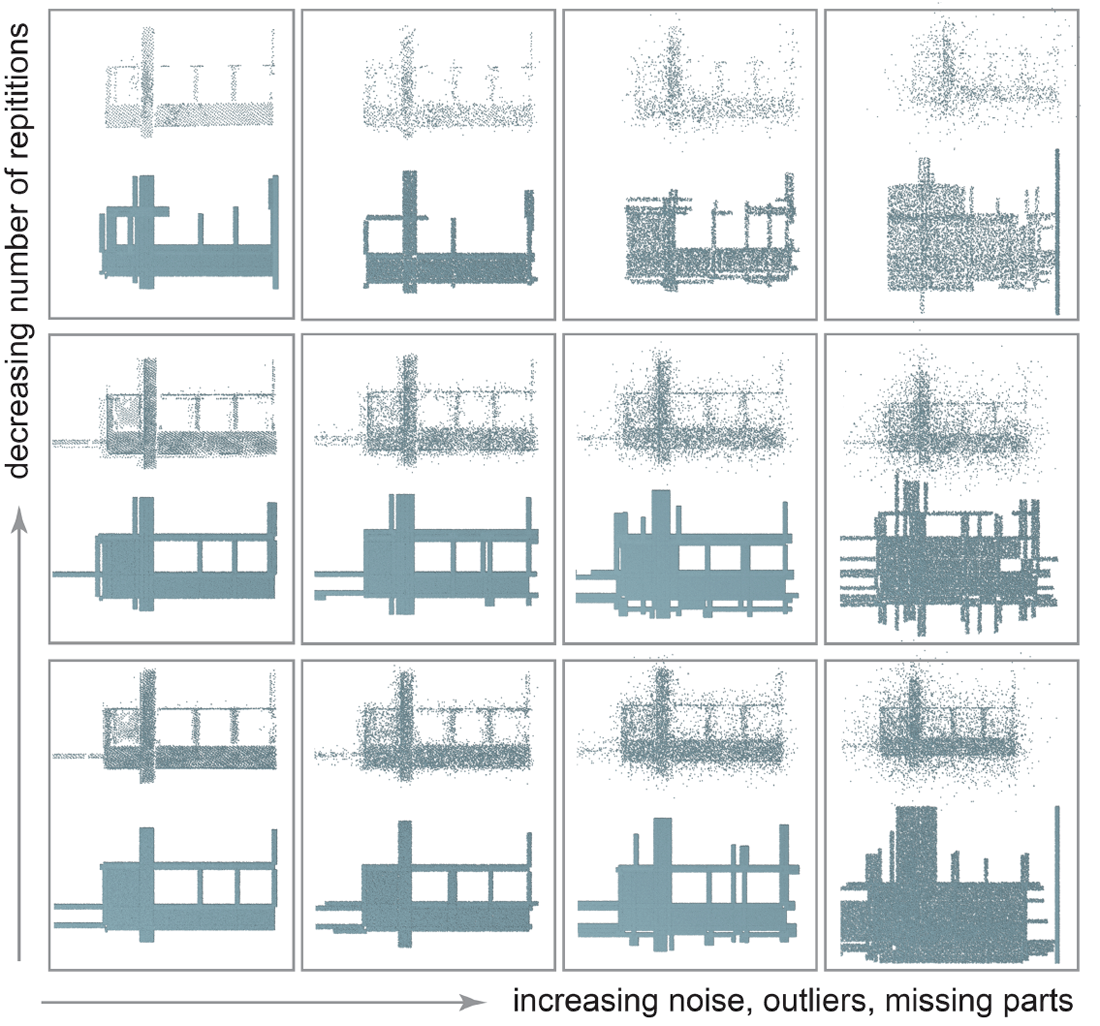
Performance of in-plane denoising with varying number
of repetitions (5, 4, 3 along the vertical direction) and increasing
amount of noise and outliers (uniform random noise 1.25%, 2.5%,
and 5% with respect bounding box diagonal length). Repeated instances
are independently generated, but of similar quality. |
|
| |
 |
|
Input and consolidation results on a building with only six floors. The consolidation result can be judged by comparing with the
photograph of the building.
|
| |
 |
|
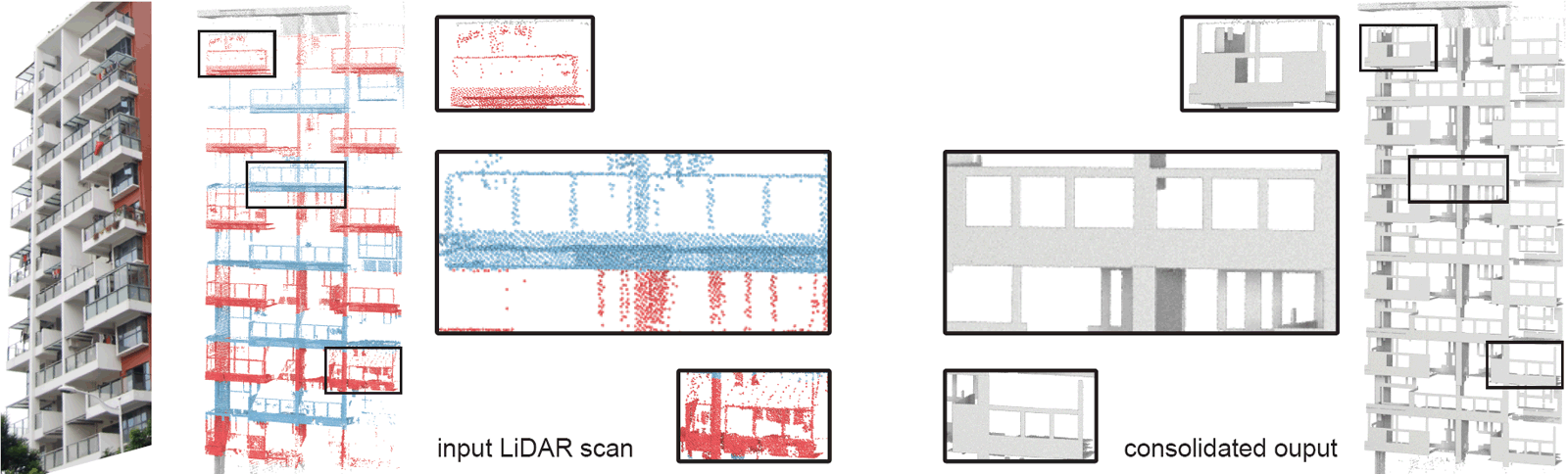
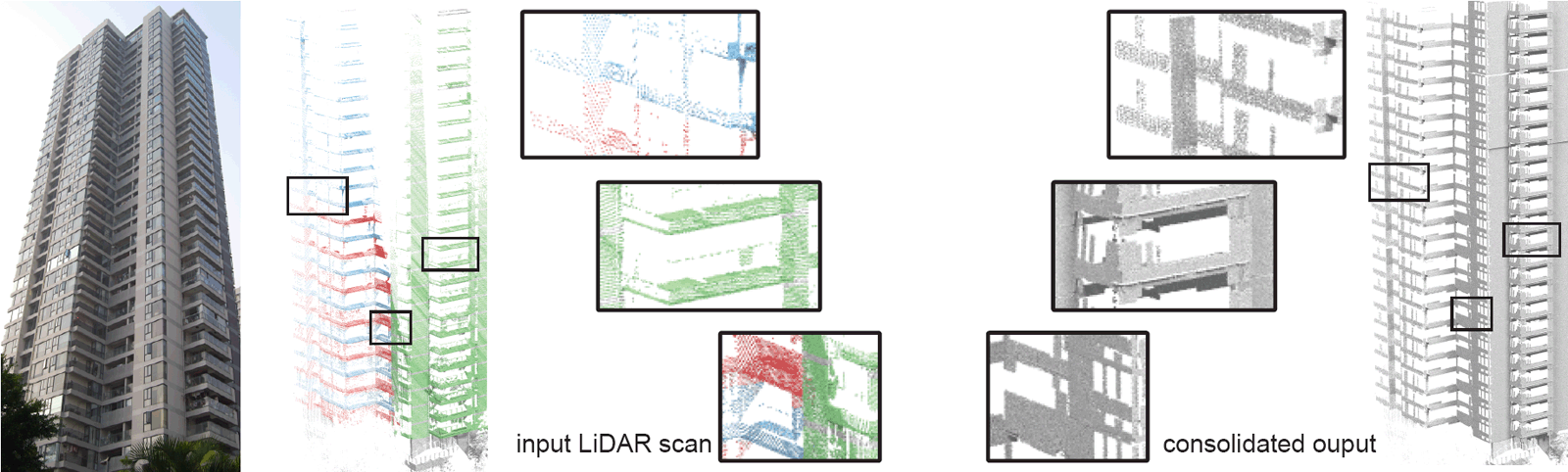
Input and consolidation results on a very tall building with progressively poor data quality with height. Even though the data
quality looks worse in comparison with the previous example, the consolidation output is superior due to the high amount of repetitions.
|
| |
 |
|
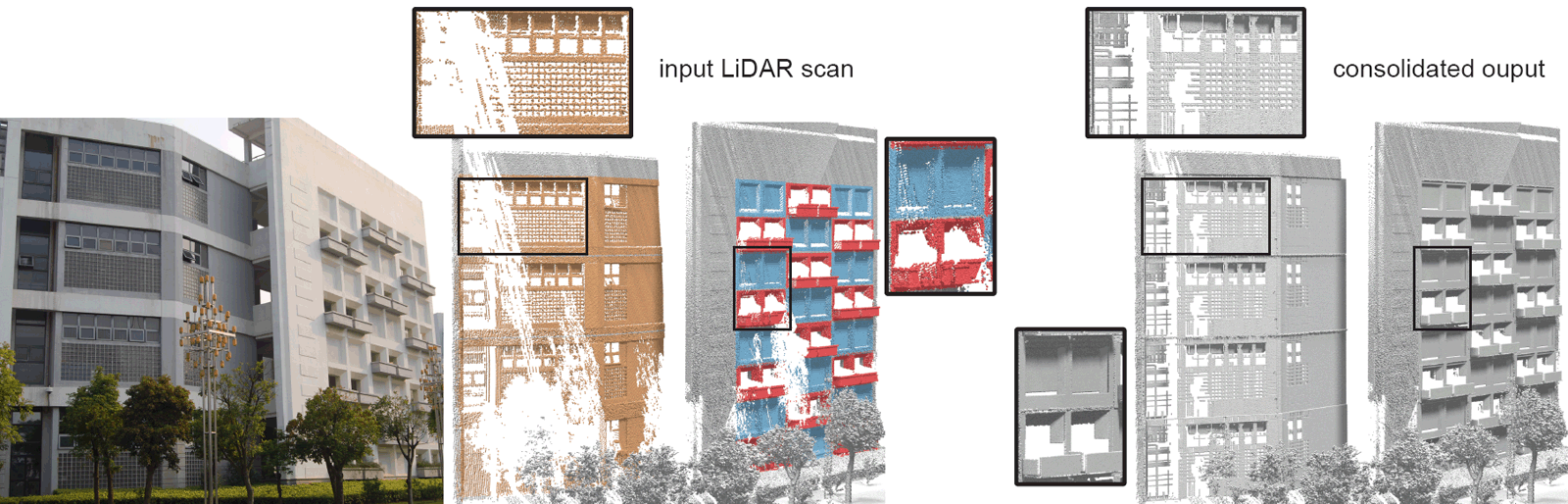
Captured walls with high detail and large noise (left) are consolidated (right), while our weighted median in-plane consolidation
preserves the fine detail (bottom zooms). In presence of high noise and large missing parts, we falsely detect additional lines (compare with
robustness results above).
|
| |
 |
|
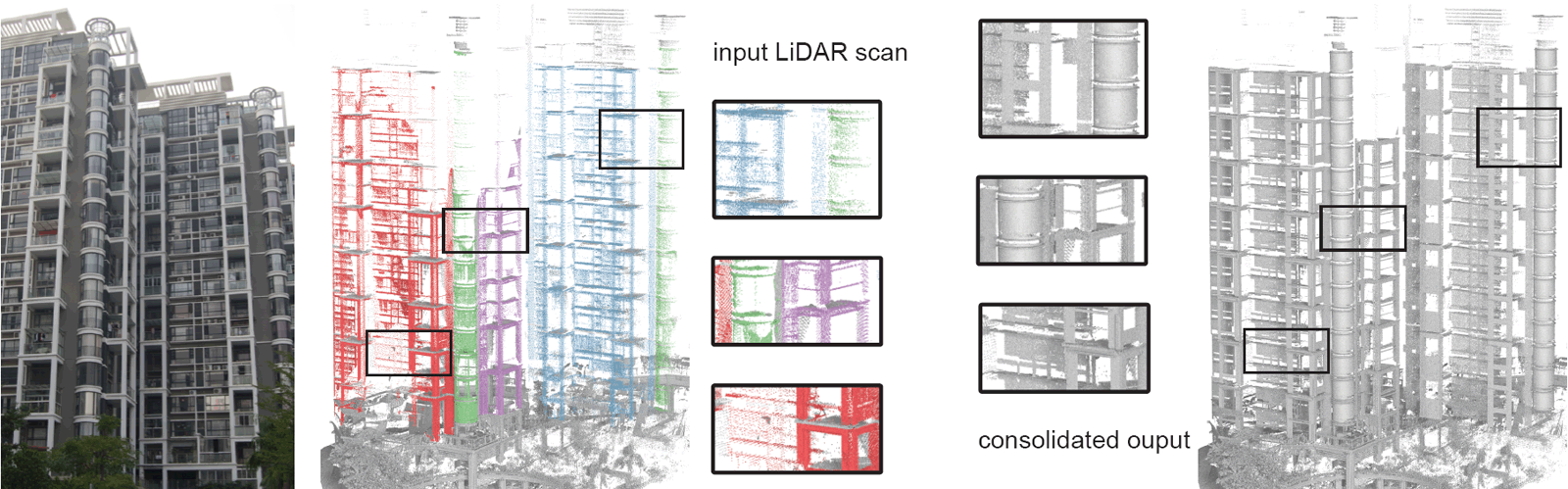
We consolidate a large urban scene, containing cylinders as a repetitive component.
|
| |
| |
Bibtex:
@article{scanConsolidation_sig_10,
AUTHOR = "Qian Zheng and Andrei Sharf and Guowei Wan and Yangyan Li and Niloy J. Mitra and Daniel Cohen-Or and Baoquan Chen",
TITLE = "Non-local Scan Consolidation for 3D Urban Scenes",
JOURNAL = "ACM Transactions on Graphics",
VOLUME = "29",
NUMBER = "4",
pages = {94:1--94:9},
articleno = {94},
numpages = {9},
YEAR = "2010",
}
 |
|
 |
|
 |
| paper (41MB) |
|
paper (8MB) |
|
slides (36MB) |
|
|





